1. Organic listings
When you’re learning how Google’s search engine works, the first step is understanding what appears in the search results.
Organic listings are the most common feature in the search results. You will always see several listings in the search results that direct you to a website.
Organic listings typically have three core components:
- Title
- Meta description
- URL

These listings are from websites that fit your search query best. Google ranks sites based on their relevance to your keyword search. The number of organic results will depend upon the search, but you’ll see numerous listings from different websites offering the answers to your query.
Can I optimize for the organic listings?
Yes! Search engine optimization (SEO) will help you rank your site better in the SERPs. You can optimize your website to help you appear in more relevant search results.
Optimizing your title
Your title is the first thing your audience sees from your organic listing. You must have a descriptive and well-thought-out title to catch your audience’s attention and get them to click on your listing.
Your title should include your keyword at the front, since this positioning helps search engines and users know that your listing is relevant to their search query.
Additionally, you’ll want to keep your title within Google’s character limits. You can use a title preview tool to ensure your title doesn’t get cut off.
Optimizing your meta description
Next, you’ll optimize your meta description. This is the paragraph of text you see below the title. People will read this preview of your page to see if it fits their search query needs.
To have an impactful meta description, you must integrate your keywords. Your keywords help your listing rank in relevant search results. These keywords also tell your audience that your listing relates to their search query.
Think of your meta description as a preview of your article. Tell your audience what they can find if they click on your link and check out your page.
Optimizing your URL
Lastly, you’ll want to optimize your URL. An SEO-friendly URL will help you perform better in the search results than one that isn’t optimized.
An SEO-friendly URL is clear and descriptive. An example is:
“www.food.com/pizza/gluten-free-pizza-recipe”
This URL is descriptive and tells your audience exactly what is on this page. They know the page contains a gluten-free recipe for pizza.
On the other hand, a URL, like “www.food.com/food/gj4939/italian-food/3941hhfkso/pizza/3920-,“ doesn’t tell your audience anything about your page. It’s a URL that’s difficult to remember and doesn’t tell your audience or search engines about your page. By optimizing your URL, you’ll help your organic listing perform better.
2. Paid advertisements
Another common Google search feature is paid advertisements. Paid advertisements, known as pay-per-click (PPC) ads, appear at the top and bottom of the search results. These paid ads drive interested leads for your business.
Paid advertisements are standard in search results. Many companies run paid ads for keywords that signify intentions to convert (or close to conversion).
Keywords like “flower shops in Harrisburg, PA” or “best places to buy a car” tend to generate traffic that looks to make a purchase.
These paid advertisements have a tag that says “ad” to indicate paid content.
Can I run a paid advertisement?
Yes! You can quickly get a paid advertisement up and running in Google’s search results.
You’ll start by deciding on the keyword or keywords that you want to target. Keywords determine where your ad appears. Once you select your keywords, you’ll bid for your ad’s placement.
You’ll then set a maximum bid, which is what you’re willing to pay when someone clicks on your ad. When you conduct keyword research, you’ll see a column for cost per click (CPC). This information helps you understand the average cost companies pay for that keyword each time someone clicks.
Your maximum bid and quality score determine placement. Your quality score combines aspects, like ad relevancy and clickthrough rate, to give your ad a score. It’s best to have a higher score with a low bid amount than a lower quality score and high bid amount.
Once you get your placement, you’ll launch your campaign.
3. Featured snippets
Aside from organic and paid listings, you’ll also see featured snippets in the search results. Featured snippets appear as a block of text that answers the user’s search query quickly. These blocks appear near the top of the search results, before the other organic listings.
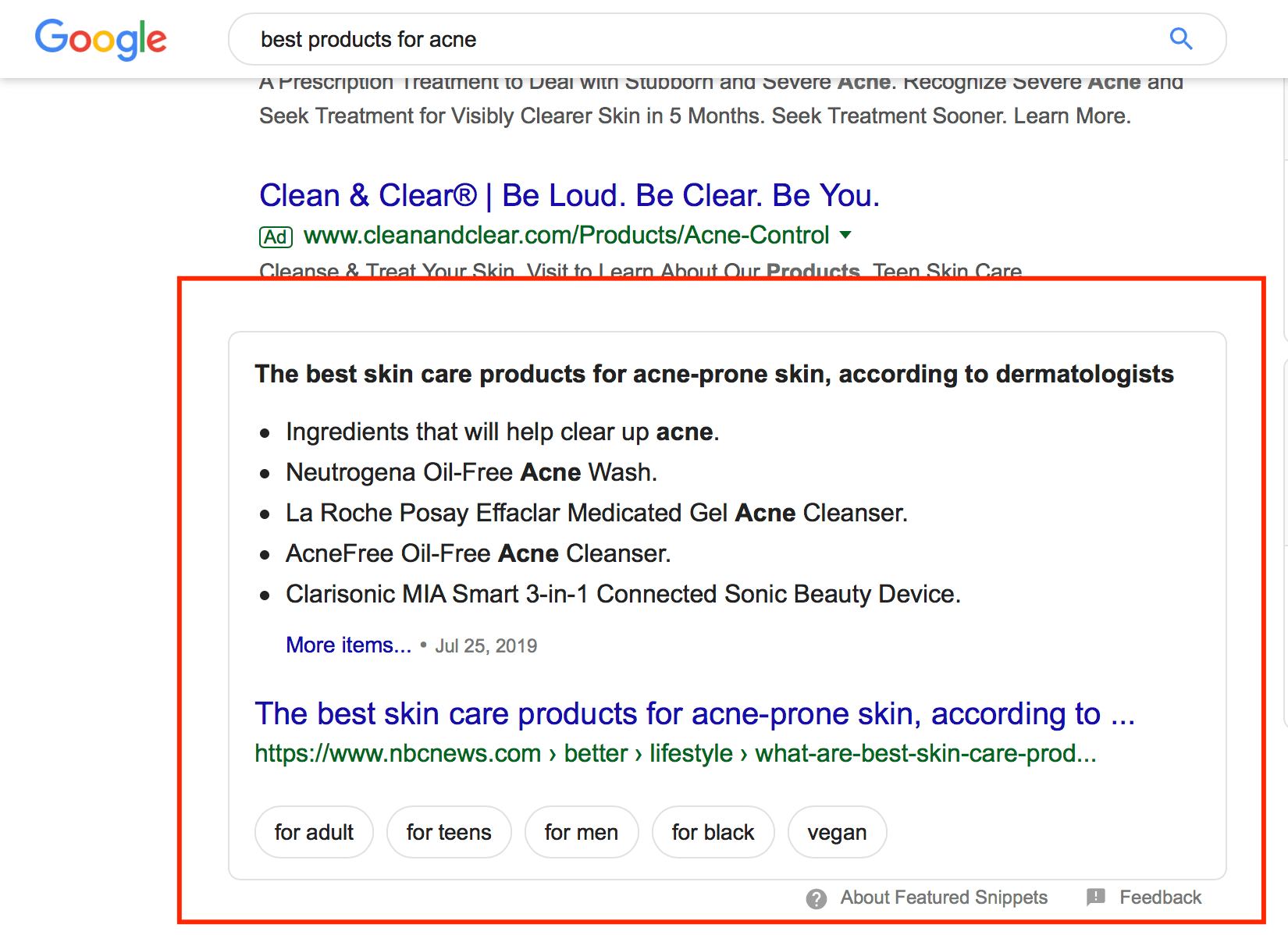
Featured snippets pull information from one of the organic listings and present it at the top of the results.
Many companies want to appear in this featured snippet since users tend to click on the first listing they see. This makes it easy to understand why the featured snippet is such a sought-after position in search results.
Can I optimize for the featured snippet?
Yes! While there isn’t any set formula for appearing in the featured snippet, you can try to structure your pages in a way that’s most likely to land you a featured snippet.
The best way to increase your chances of appearing in a featured snippet is through clear and concise writing. Featured snippets focus on providing users with information fast.
For example, let’s say you’re trying to appear in the featured snippet for the question: “What’s the best way to raise my credit score?” A quick way to answer this question is to create a bulleted or numbered list of ways to improve your score.
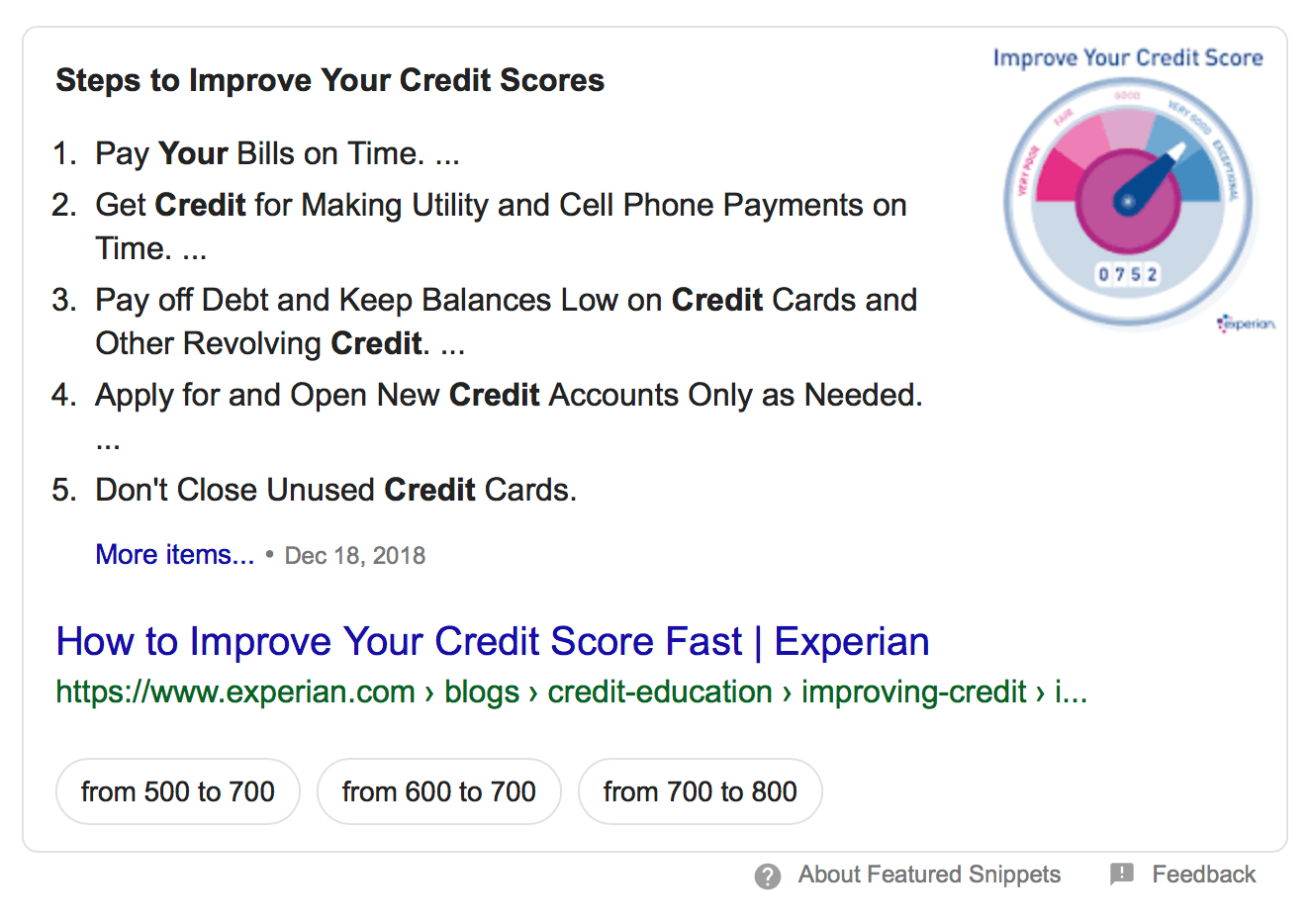
In this example, Experian answers the user’s question quickly by creating a numbered list of ways to improve credit score. This list is perfect featured snippet material because it provides the user with a fast, digestible answer to their question.
If you want to have an opportunity to appear in more featured snippets, optimize your text to answer user’s questions quickly and provide them in a digestible format.
4. Knowledge graphs
A knowledge graph is a box that appears on the right-hand side of the search results. This box contains necessary information about companies, celebrities, historical figures, and more.
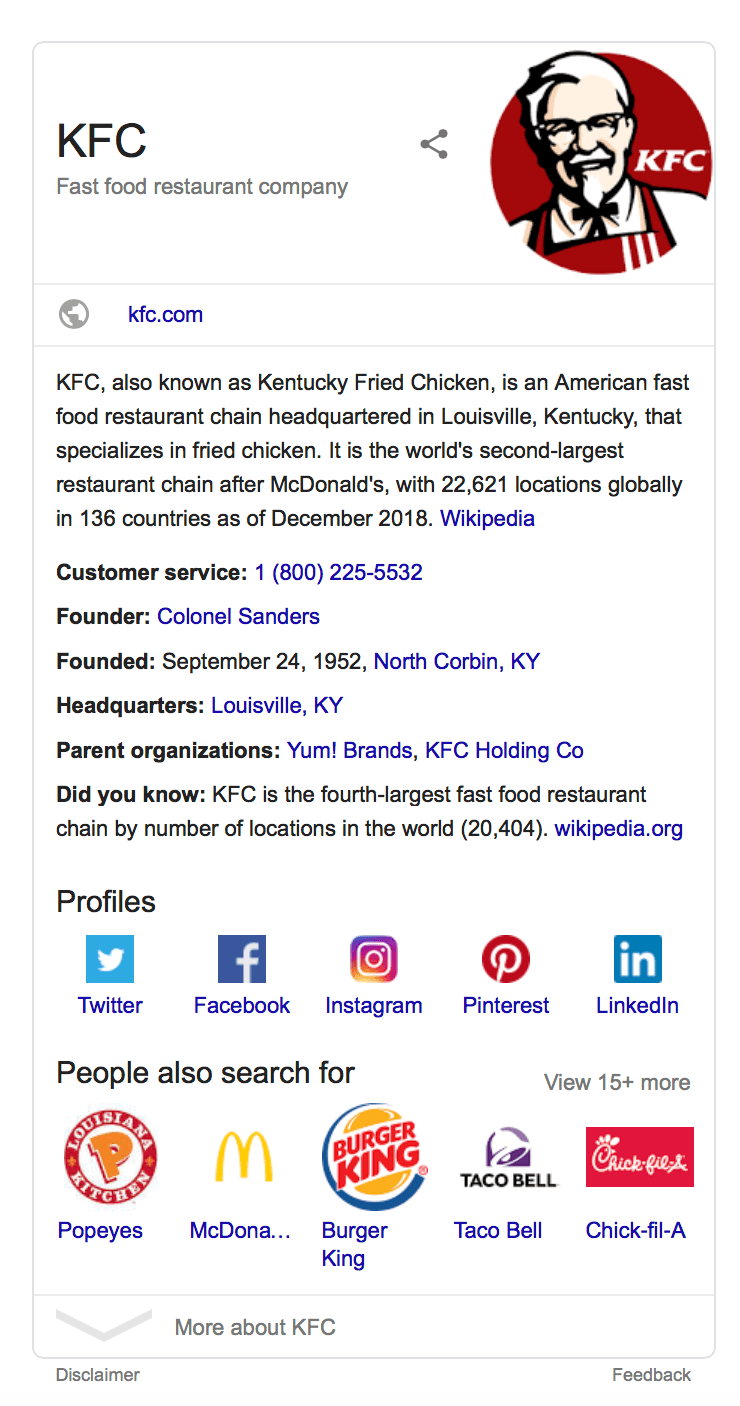
The information for knowledge graphs typically comes from sources like Wikipedia. As the name suggests, this section provides users with basic knowledge about a specific topic. It can be background on a person, place, or event, or quick information about something.
Knowledge graphs tend to appear in generic search queries. For example, if you search “George
Washington,” you get a knowledge graph that provides basic information about him.
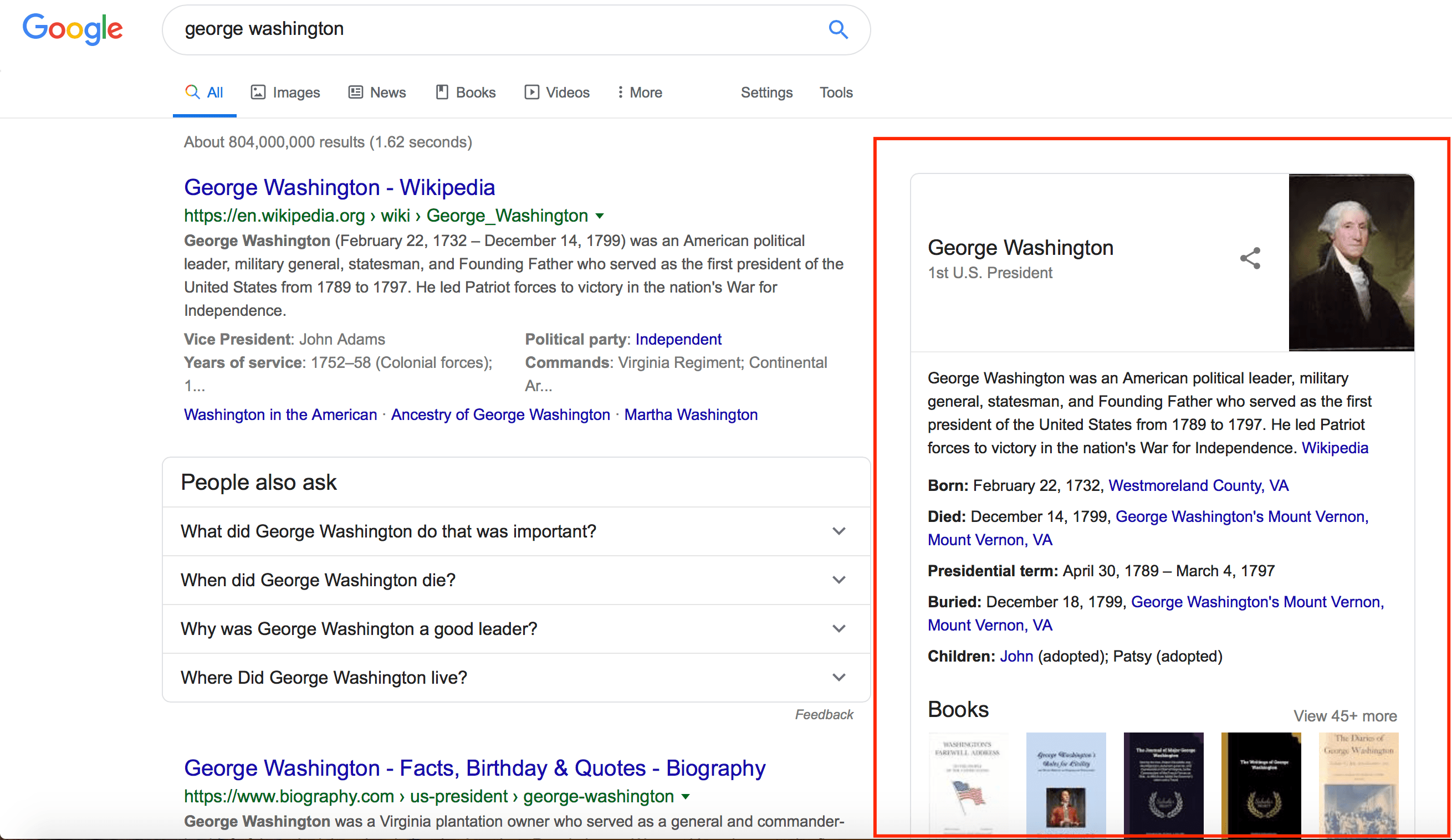
The knowledge graph is great for users who want basic information.
Can I optimize for knowledge graphs?
No. Unfortunately, Google compiles the information and doesn’t typically pull data from your website. It relies on sources like Wikipedia to great these knowledge panels, so there isn’t any way for you to optimize your site to appear in this panel.
5. “People also ask” section
When you search Google, you’ll see a box where people ask questions related to the topic. These boxes can appear regardless of whether someone asks a question or plugs in a keyword into the search bar.
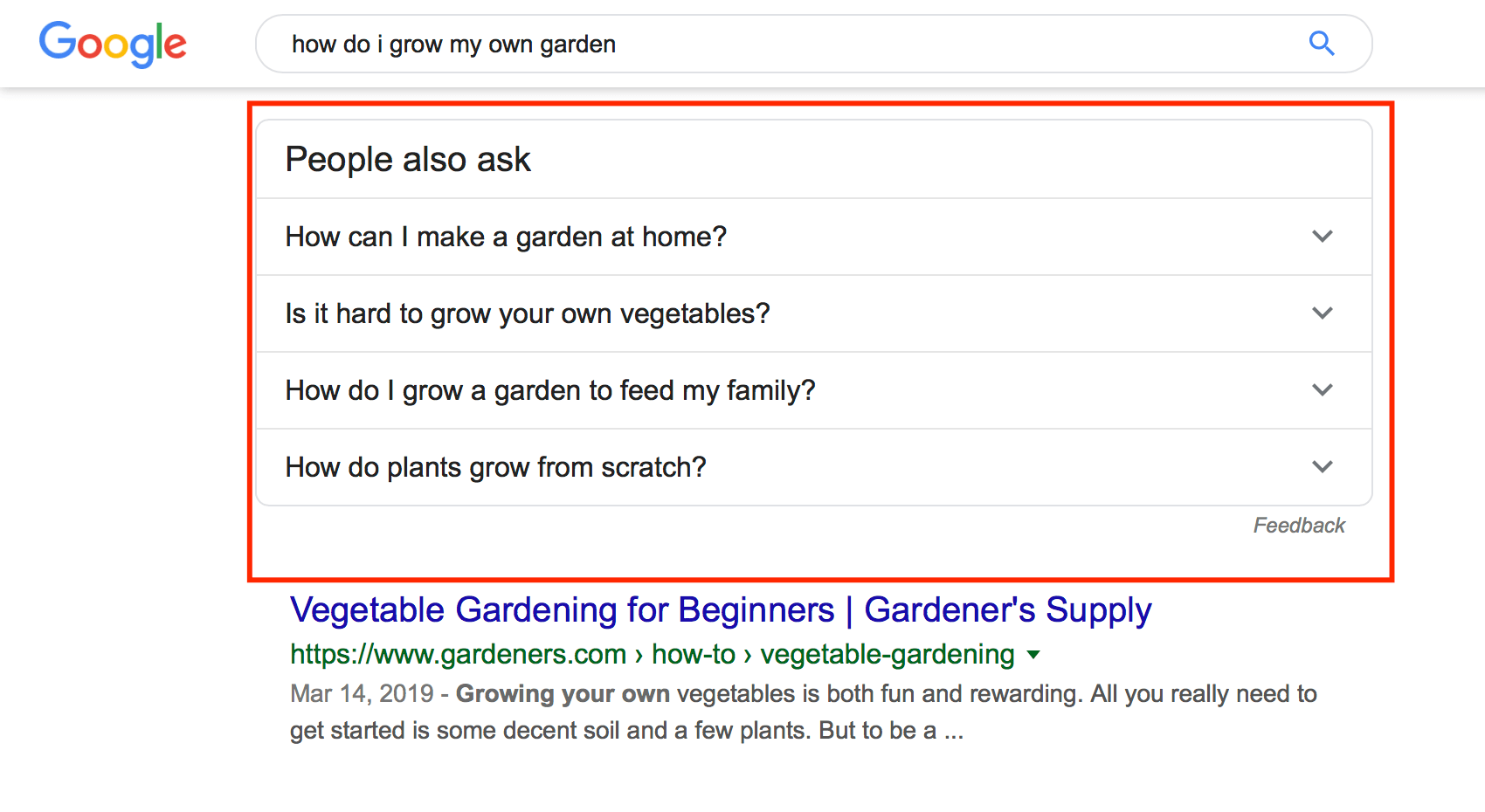
The people also ask section provides users with additional, common questions people ask about a topic. This section helps answer questions users may have in addition to their original search query.
If a user clicks on one of the questions, they’ll get an answer and see a link to the source of the solution. The user can also conduct a new search query based on that question.
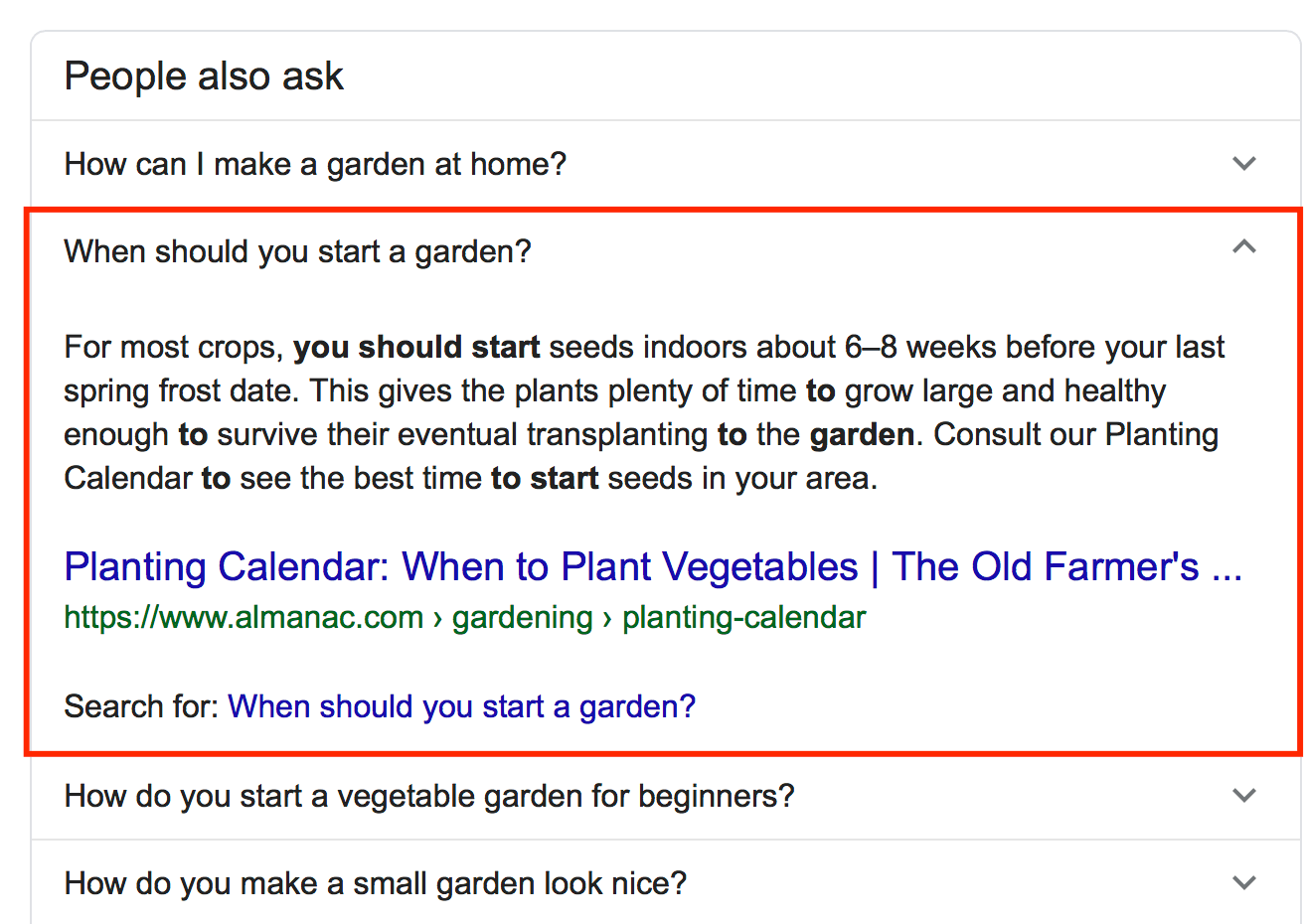
Can I optimize for the people also ask section?
Maybe. It isn’t entirely clear which questions will appear in the people also ask section. In most cases, the answer comes from the featured snippet of that search query, so you can try to optimize to get into the featured snippet for that particular search query.
For example, if someone searches “gardens at home,” the question “when should you start a garden,” appears in the people also ask section. If you choose to conduct a new search query on “when should you start a garden,” the answer from the people also ask section appears as the featured snippet on the new search query page.
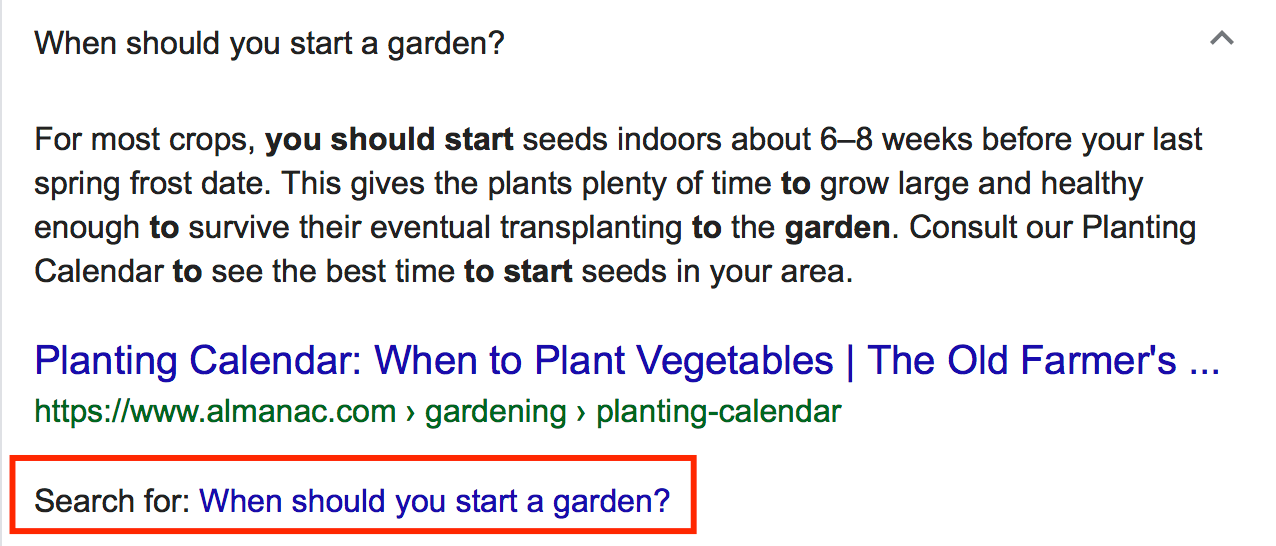
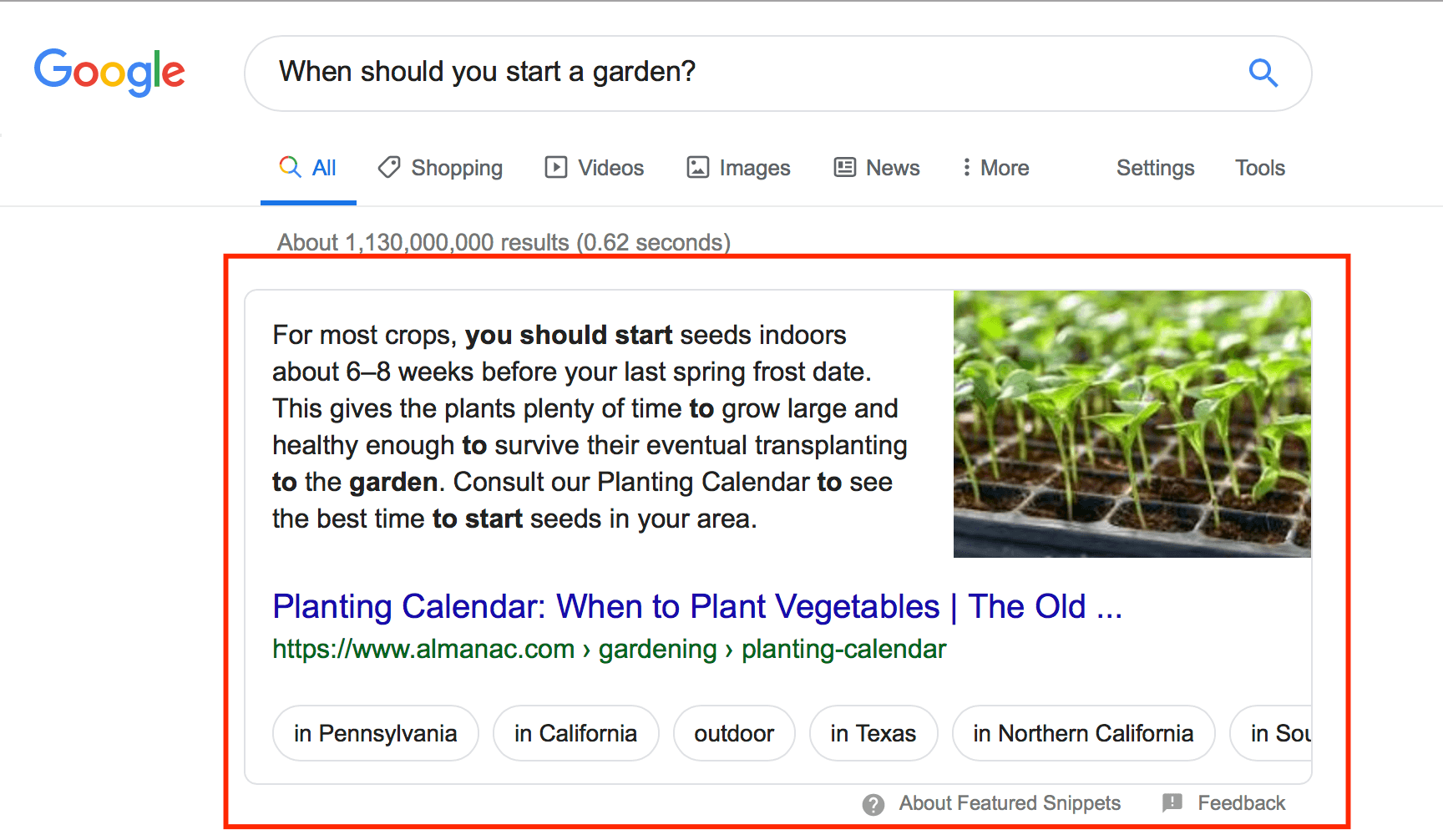
While you may not be able to determine which questions will appear in the people also ask section, you can work to optimize to get the featured snippet position. This practice may help you appear in the people also ask section for related queries.
6. Local SEO 3-pack
Users that conduct a local search will generate the local SEO 3-pack. This box appears at the top of the search results and lists three local businesses that fit the search query. The local SEO 3-pack helps drive local traffic for your business.
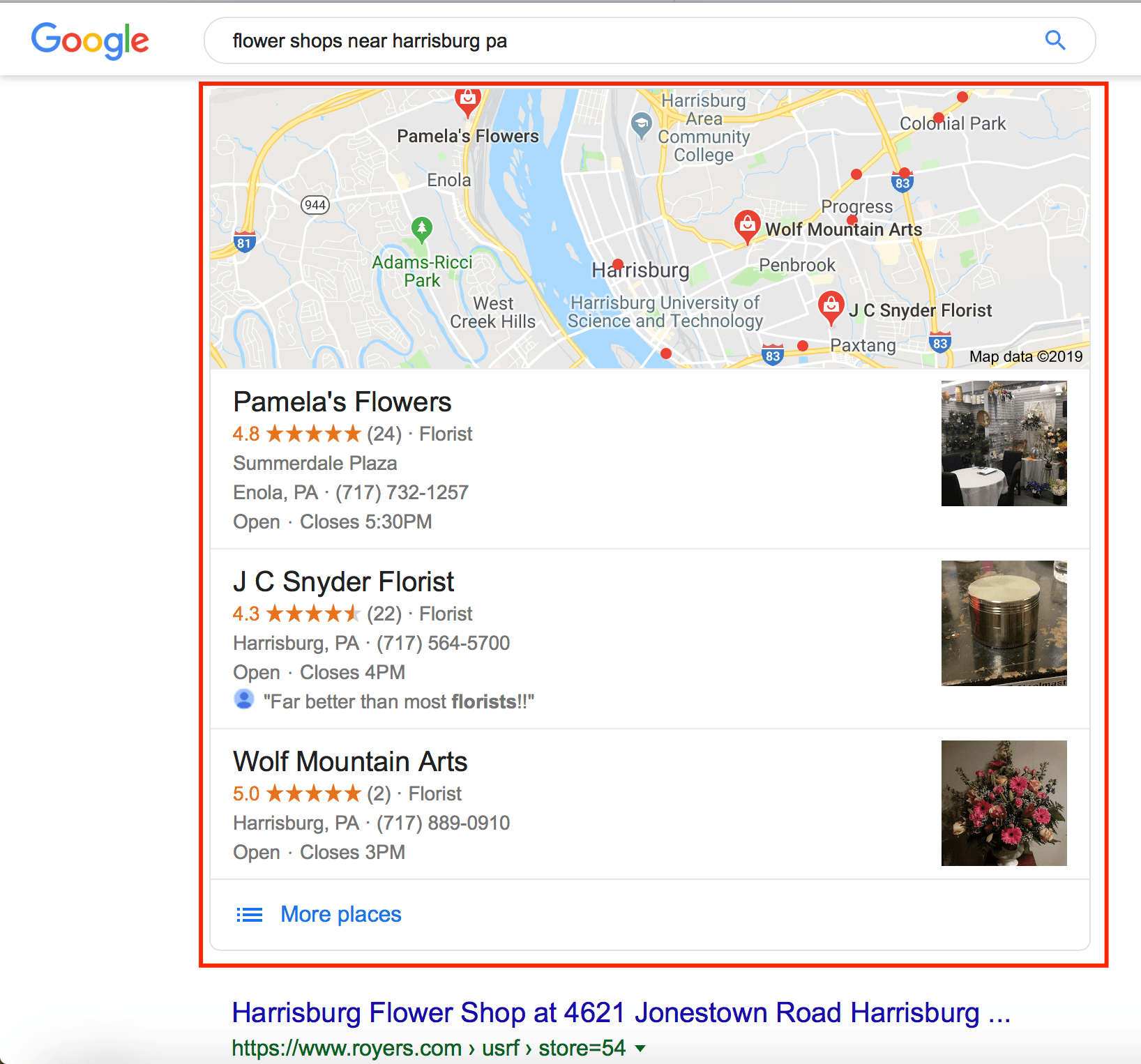
As you learn more about how Google’s search engine works, you’ll find that the local SEO 3-pack appears at the top of the local search results. It’s an excellent position for local businesses looking to drive more foot traffic.
Can I optimize for the local SEO 3-pack?
Yes. While there isn’t anything you can do that will guarantee you get in the local SEO 3-Pack, you can increase your chances of appearing in it by optimizing your local listing.
Claim your local listing through Google My Business’s site. Once you’ve claimed your listing, you’ll want to fill out all the information on it. Verify all the information, like your name and address, is correct and that you have photos on your listing.
A complete listing boosts engagement on your local listing. It’s a great way to help you appear in the local SEO 3-pack.
7. Carousels
Carousels are one of the Google search features that appear at the top of the search results. It’s a line of images that relates to the search query.
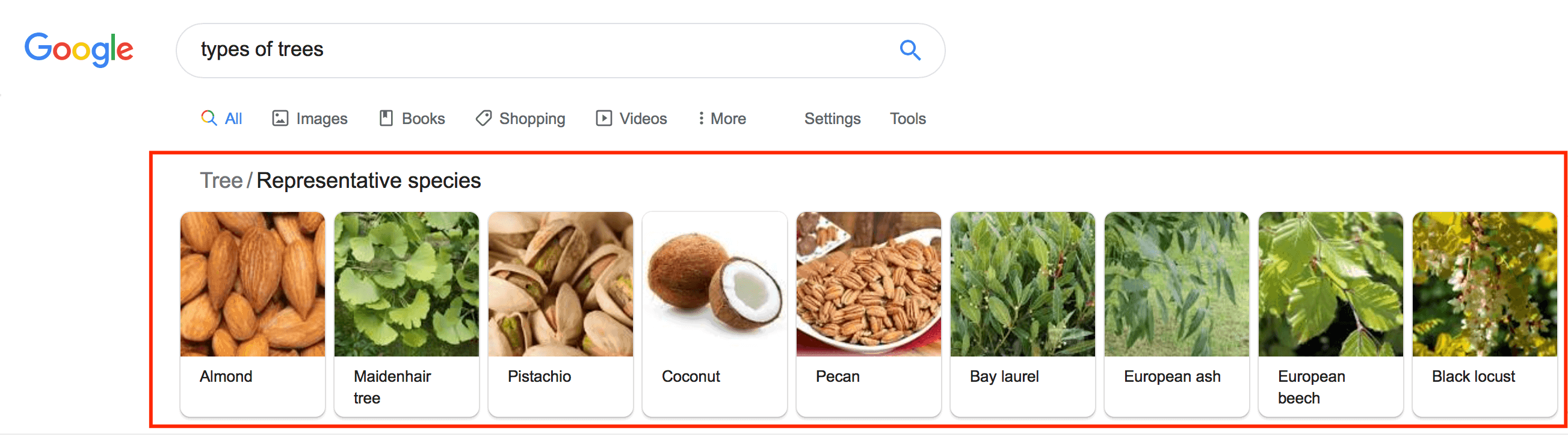
Carousels have clickable images that the user can click on to find more information. In this example, the user could click on the “almonds” picture and find more information about almonds.
Can I optimize for a carousel?
No. Carousel images are generic posts that don’t link back to a business or website.
8. Video results
When a user searches, some search results may generate a few related videos to the topic. These videos typically come from YouTube. The user may see one or a few thumbnails of videos.
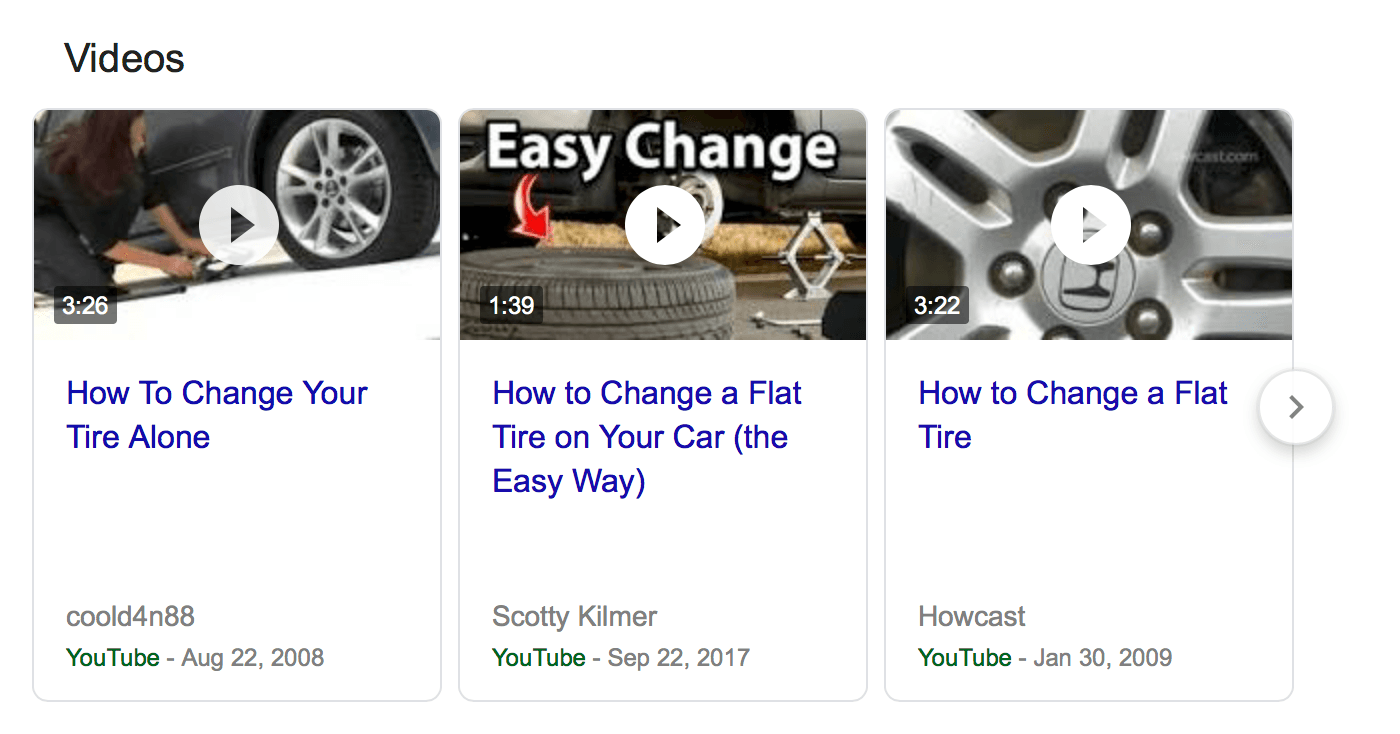
Videos commonly appear in searches where users ask how to do something. The title, tags, and description from the video determine if it’s a good fit for the search results.
Can I optimize my videos to get them into Google search results?
Yes. While it isn’t a guarantee, you can take steps to help your videos be more likely to appear in search results.
If you have how-to type videos, you can optimize them to help make them more likely to appear in the search results. Optimize the title, tags, and description to include relevant keywords related to your video. It will help your video appear in search results.
9. Twitter posts
If you search for a business or famous person, you may see tweets from Twitter in the search results. Whether it’s their own Twitter account or people talking about them, you see a preview of three tweets.
Tweets will only appear for branded searches. So, unless someone searches your brand specifically, they won’t see your tweets.
Can I optimize to get my tweets in Google?
Not really. The only “optimization” you can do is have an active presence on Twitter. If you’re tweeting consistently and tweeting recent information and events, users will see the most recent information in the search results.
If you have an active Twitter presence, you may make leads more likely to click on your tweets and check out your business on social media.
10. Answer boxes
Answer boxes appear in the search results when users ask a question that contains public domain knowledge. They provide searchers with quick information.
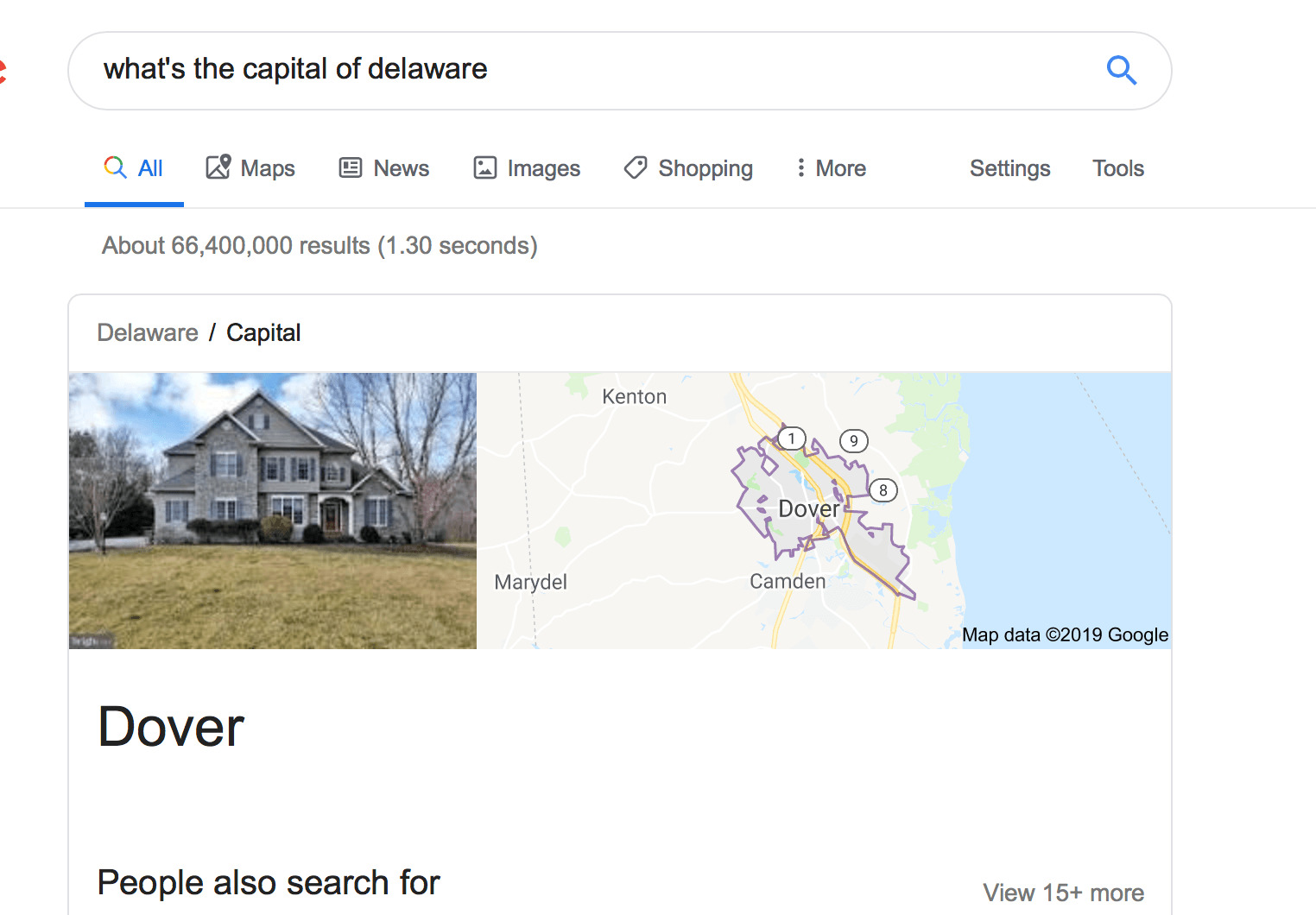
These answer boxes only appear when users ask common questions. Questions like “who was the 32nd President of the United States?” or “what’s the capital of Delaware?” typically generate an answer box.
Can I optimize for the answer box?
No. Google generates the information in these boxes from public domains of knowledge.
11. Product shopping and showcase shopping ads
Product shopping and showcase shopping ads are two more Google search features you’ll see in search results. We’ve paired these two together because they both share a similar purpose.
Product shopping ads typically appear when someone knows what they want to buy but haven’t determined where to buy it. The product shopping ads provide users with options for different places they can buy it.
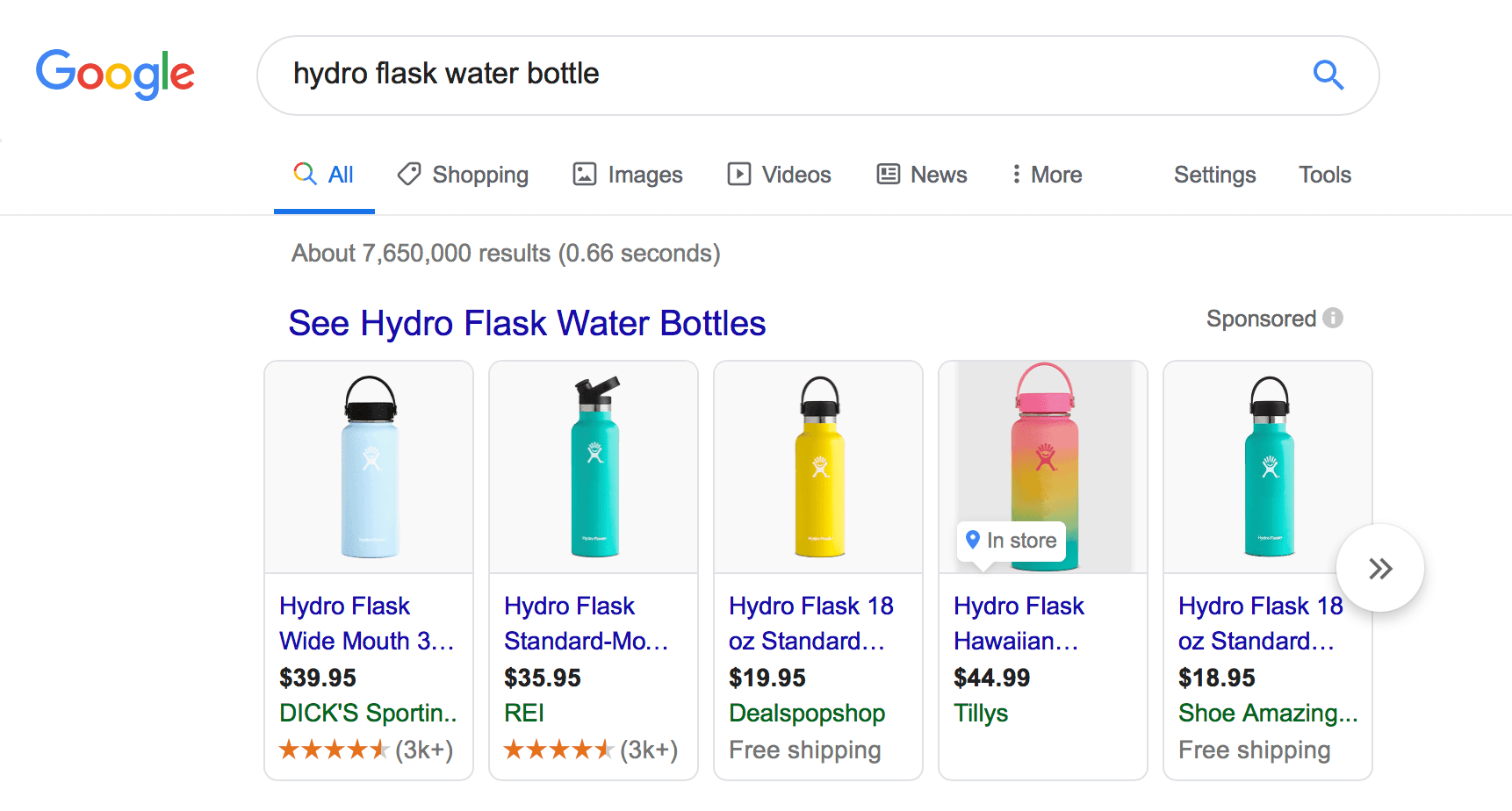
The listing includes a photo of the product, the retailer, and the price. Some listings may also include a star rating or feature like free shipping.
Showcase shopping ads appear almost identical to product shopping ads. The only difference with these ads is that the intent is different. Showcase shopping ads appear when users don’t know exactly which product they want or where they want to get it.
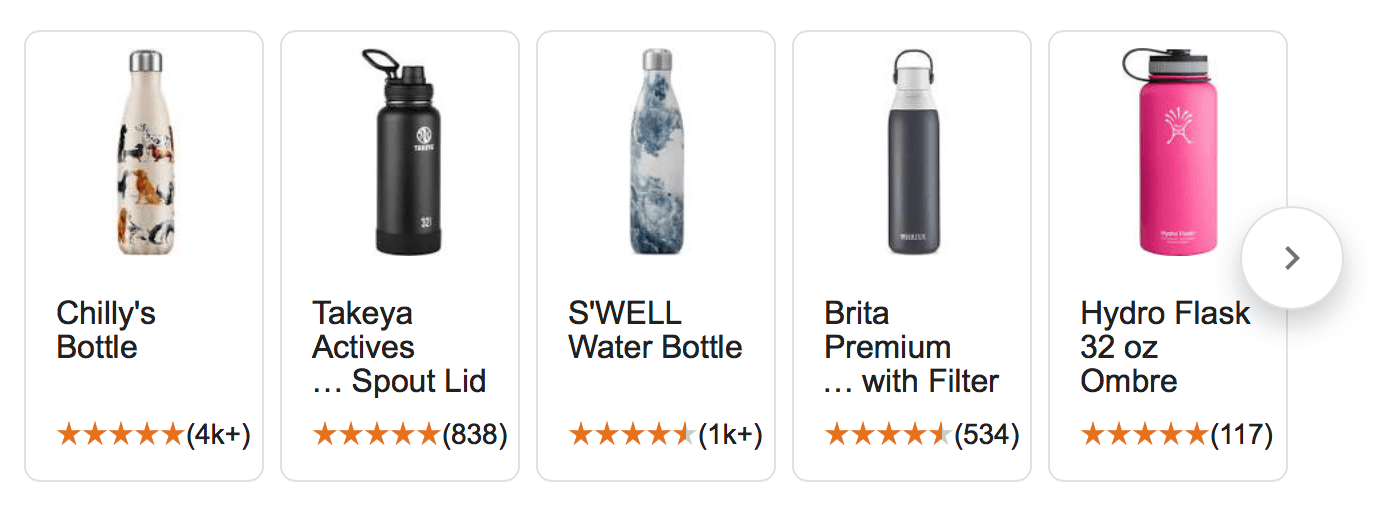
For this search result, users will see the same product from different brands. It helps them figure out which brand they like best, so they can then find the right place to buy it.
Can I optimize for product or showcase shopping ads?
Yes. You can create your product or showcase shopping ad to appear in search results. Similar to PPC, you’ll bid for the cost each time someone engages with your ad. You’ll set up your ad by choosing a title and photo for the product.

